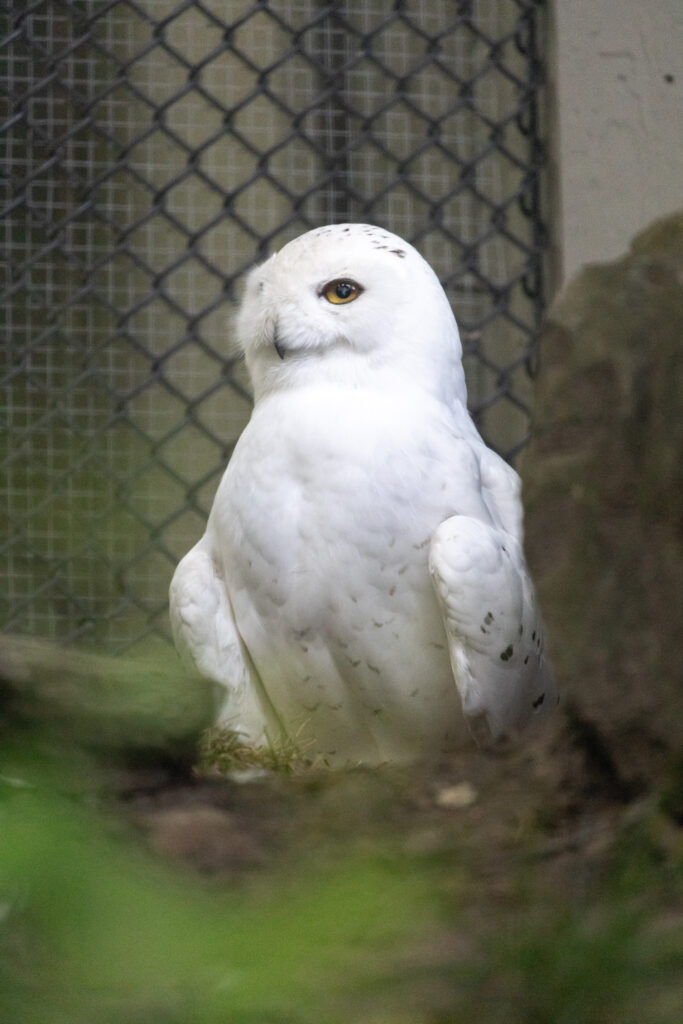
Working with birds is fun, but does have challenges as well! Here at the Zoo we have many different birds in our care. In our education building, which is not open to the public, we have psittacine birds (parrots). These birds partake in education programs and the Zoomobile. We have raptors (birds of prey), which includes the snowy owls and red-tailed hawk. The Savanna Aviary contains spotted dikkops (a shore bird), sandhill cranes, and multiple species of passerines (perching birds/song birds). Of course, we also have African penguins in the Rocky Coast area too!
Birds have many unique adaptations. They all have feathers which serve as insulation, aid in flight (or swimming for the penguins), and can serve as signals to other birds. Birds go through molt, which is when they lose old feathers and grow new ones. Some birds do this gradually, but some birds molt all their feathers at once. African penguins are a species that molts all at once so you may see some of them looking quite bald like little vultures. These birds are not sick, they are just molting their feathers! When new feathers first grow in, they are connected to blood vessels and are called a “blood feather.” Once the feather is fully grown, it loses the blood supply. However, if a feather breaks while it still has a blood supply it can bleed a large amount. When this occurs, we need to remove the feather to stop the bleeding. This can happen to pet birds too and is one of the most common pet bird emergencies.
Most birds also have hollow bones to reduce their weight for flight. Penguins and other flightless birds are an exception to this and have solid bones like us. Birds do not have a diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest and abdomen in mammals. They do have air sacs which help to increase airflow through the respiratory system and keep a higher oxygen flow into the body.
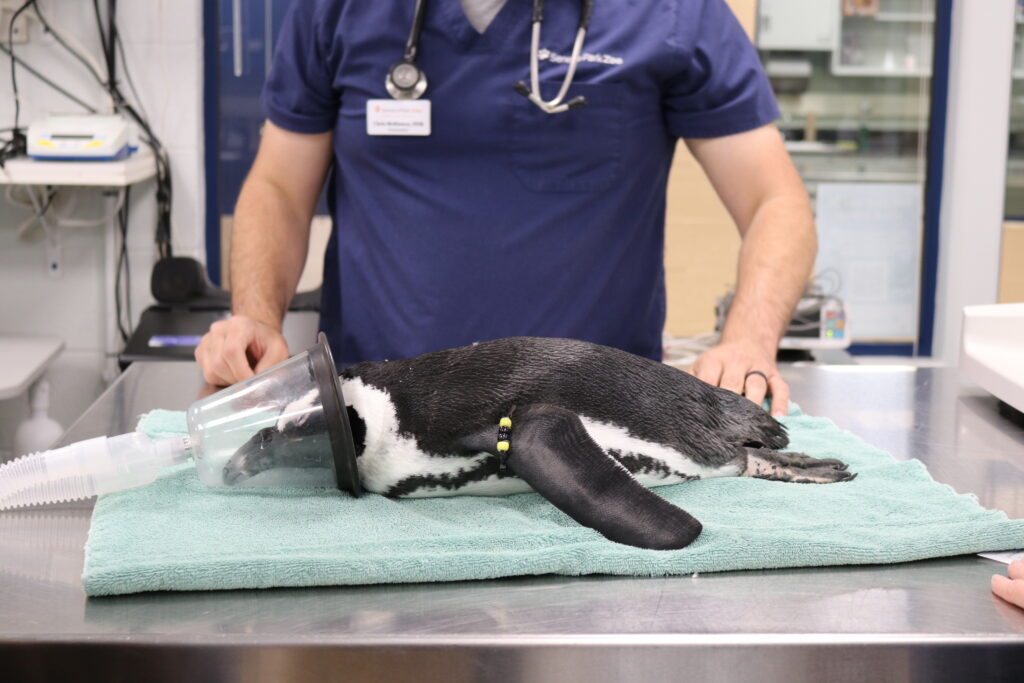
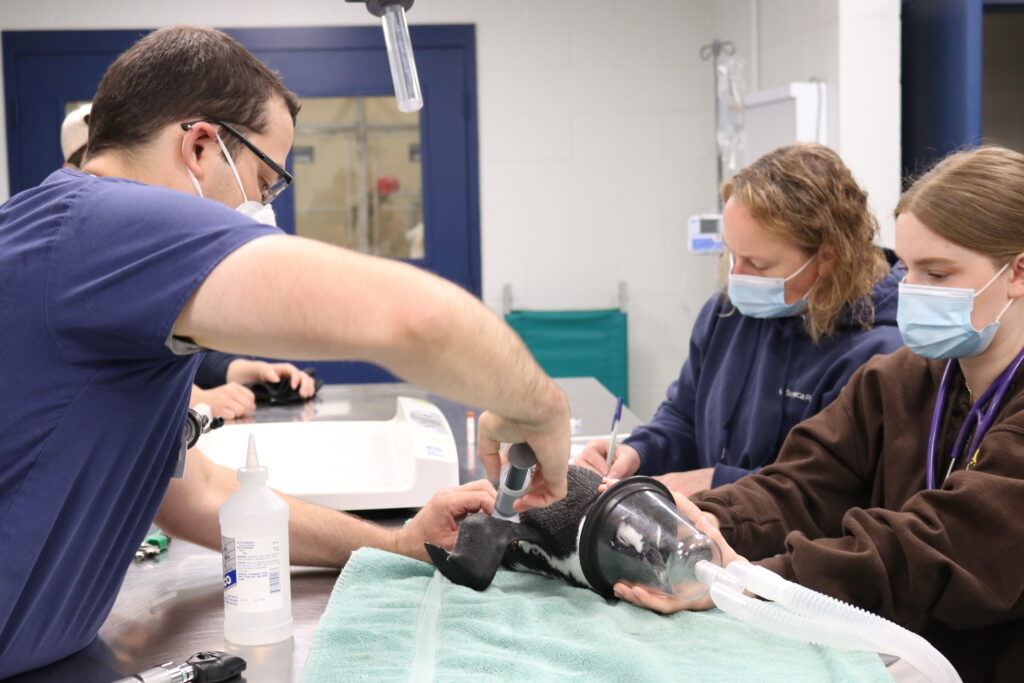
It is important for our safety and the safety of the birds to be aware of how a bird might act when we handle them for veterinary procedures. For long procedures, we will anesthetize the birds. This reduces the risk of them injuring us and reduces that risk that they injure themselves trying to escape. Most birds first instinct when we restrain them for an exam, nail trim, or to draw blood is to flap their wings to try to get away. This can cause injury to the wings so we cover their wings with a light towel. Parrots might try to bite while raptors will try to use their talons for defense.
All of the birds that go outside receive a vaccine for West Nile Virus. This virus is spread by mosquitos and can cause neurological disease in many different animal species. Penguins are also prone to another mosquito borne disease called avian malaria. This is a parasite that only infects birds. This disease was very rare in the northern US, but is becoming more common because climate change is leading to longer mosquito seasons and different species of mosquitos moving further north. To protect them, the penguins receive a preventative medication during mosquito season.


The highly efficient respiratory tracts of birds make them prone to respiratory infections. One that has been in the news lately is avian influenza. The Zoo has a plan in place to help protect our birds from this virus. This plan was developed through discussions with veterinary teams at other zoos and the NY state veterinarian. They can also get a fungal infection called Aspergillosis. This is a fungus that exists in the soil and can infect birds when they are stressed or ill with another disease.
Birds hide signs of illness very well because in the wild, if they show signs of weakness, they become a target for predators. Because of this adaptation, we regularly evaluate all of our birds. They receive an overall annual checkup and the keepers give daily reports on anything abnormal so that we know if a bird needs additional exams or tests such as blood work or x-rays. The bird’s weights are also monitored. If a bird does need any tests performed, we bring them to the Animal Hospital. X-rays allow us to not only see the bones but also the outline of the heart, liver, and other internal organs. Some diseases will cause enlargement of organs which we can see on the x-rays. The blood allows us to check the red and white blood cells along with enzymes that show liver and kidney health, protein levels, and electrolytes.
Stop by and visit with the man species of birds in our care this weekend and all throughout the year!